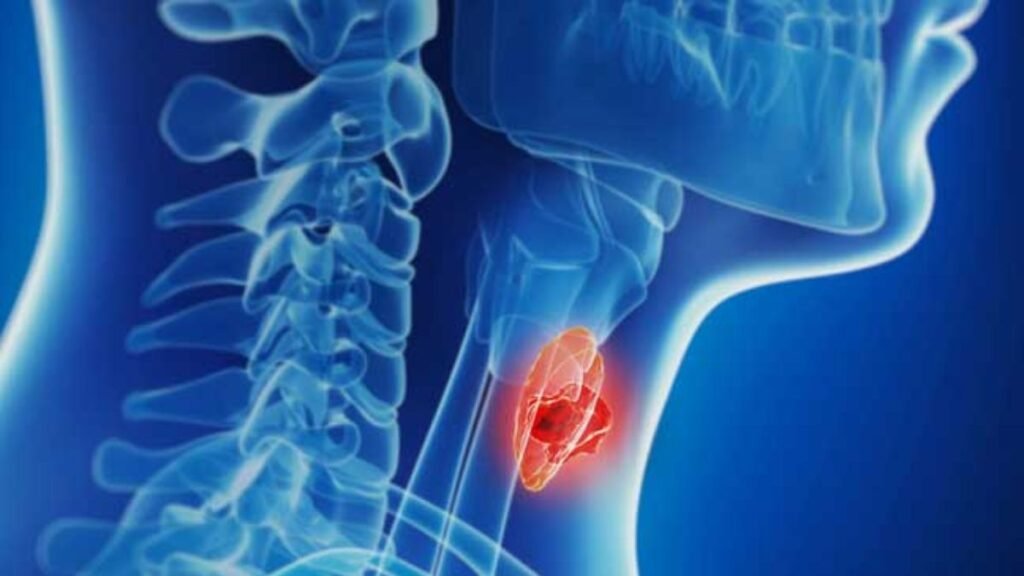
Overview
Thyroid cancer arises in the cells of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and other bodily functions.
Though thyroid cancer is relatively rare compared to other types of cancer, its incidence is on the rise globally.
The disease can be challenging to detect in its early stages as it often presents without symptoms, but with advances in diagnosis and treatment, most cases of thyroid cancer are treatable, especially when detected early.
In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures related to thyroid cancer.
Table of Contents
What Is Thyroid Cancer?
Thyroid cancer occurs when cells in the thyroid gland mutate and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor.
There are several types of thyroid cancer, categorized based on how the cells appear under a microscope.
However, the four main types are:
- Papillary Thyroid Cancer (PTC): The most common form, accounting for around 80% of thyroid cancers. It typically grows slowly and often spreads to lymph nodes.
- Follicular Thyroid Cancer (FTC): This type accounts for about 10-15% of cases and is more likely to spread to distant organs, such as the lungs or bones.
- Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC): MTC makes up about 2-3% of cases and originates from C cells that produce calcitonin. It can be hereditary or occur sporadically.
- Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A rare and aggressive form of thyroid cancer that accounts for less than 2% of cases. It grows quickly and is challenging to treat.
Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as the tumor grows, it can present several signs, including:
- Lump or Swelling in the Neck: A painless lump or nodule in the front of the neck is often the first sign.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing: Enlarged tumors can press against the windpipe or esophagus.
- Persistent Hoarseness or Voice Changes: Tumors pressing on the vocal cords may cause changes in voice.
- Neck Pain: Pain in the neck, jaw, or ears may develop as the disease progresses.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck can indicate the spread of cancer.
Causes of Thyroid Cancer
The exact cause of thyroid cancer remains unclear. However, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- Genetic Factors: A family history of thyroid cancer or genetic syndromes, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndrome, can increase risk.
- Radiation Exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation, especially during childhood, is linked to an elevated risk of thyroid cancer.
- Iodine Deficiency: A lack of iodine in the diet may contribute to certain types of thyroid cancer.
- Gender and Age: Women are more likely to develop thyroid cancer, with higher incidence rates occurring between ages 30 and 60.
- History of Thyroid Conditions: Conditions such as goiter (enlarged thyroid) or thyroid nodules may increase susceptibility.
Risk Factors for Thyroid Cancer
Several risk factors are associated with thyroid cancer:
- Radiation Therapy to the Head or Neck: Past exposure to radiation increases the likelihood of developing thyroid cancer.
- Hereditary Conditions: Certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of medullary thyroid cancer.
- Age and Gender: Women and older individuals are at higher risk.
- Family History: A family history of thyroid cancer, thyroid disease, or certain genetic conditions may predispose individuals.
Complications of Thyroid Cancer
- Metastasis: Thyroid cancer can spread to other organs, such as the lungs, bones, or lymph nodes.
- Voice and Swallowing Changes: Surgery may affect the nerves controlling the vocal cords, causing hoarseness or difficulty swallowing.
- Recurrence: Thyroid cancer may return even after successful treatment, necessitating ongoing monitoring.
- Hypothyroidism: Removal of the thyroid gland often leads to hypothyroidism, requiring lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Cancer
Diagnosing thyroid cancer involves several steps:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider examines the neck for lumps or enlarged lymph nodes.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound helps determine the size, shape, and characteristics of thyroid nodules.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: A thin needle extracts cells from the nodule for microscopic examination to determine if they are cancerous.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests assess levels of thyroid hormones, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and calcitonin.
- Radioactive Iodine Scan: This imaging test evaluates thyroid function and helps detect cancer spread.
- CT or MRI Scans: Advanced imaging tests may be used to check for cancer spread beyond the thyroid.
Treatment for Thyroid Cancer
The treatment approach depends on the type, size, and stage of thyroid cancer. Common treatments include:
1. Surgery:
- Thyroidectomy: Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland. Total thyroidectomy involves removing the entire gland, while a lobectomy removes one thyroid lobe.
- Lymph Node Removal: If cancer has spread, lymph nodes in the neck may be removed.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy (RAI): After surgery, radioactive iodine may be used to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
3. Hormone Therapy: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy helps maintain normal hormone levels and may also suppress the growth of cancer cells.
4. External Beam Radiation Therapy: Rarely used, this therapy targets cancer cells with high-energy beams.
5. Chemotherapy: Primarily used for advanced or anaplastic thyroid cancer that does not respond to other treatments.
6. Targeted Therapy: Medications that specifically target cancer cells may be used for advanced cases.
Prevention of Thyroid Cancer
Although thyroid cancer cannot always be prevented, some strategies may help lower risk:
- Minimize Radiation Exposure: Avoid unnecessary radiation exposure, especially in childhood.
- Iodine-Rich Diet: Ensure adequate dietary iodine intake through iodized salt, seafood, and dairy products.
- Regular Screening: If you have a family history of thyroid cancer or genetic syndromes, regular screenings may help detect cancer early.
- Genetic Counseling: If you have a family history of medullary thyroid cancer, consider genetic counseling to assess and manage your risk.
Conclusion
Thyroid cancer, though relatively rare, is often treatable, especially when detected early.
Understanding the risk factors, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical attention are critical for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
With advances in surgical techniques, radioactive iodine therapy, and targeted therapies, many individuals diagnosed with thyroid cancer can lead full and healthy lives.
Regular follow-up care and a healthy lifestyle contribute to long-term management and improved outcomes.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of thyroid cancer?
The main types are papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer.
2. Can thyroid cancer be cured?
Yes, especially when detected early, thyroid cancer is highly treatable and often curable.
3. How is thyroid cancer detected?
A combination of physical exams, imaging tests like ultrasound, and biopsies are used to detect thyroid cancer.
4. Who is at the highest risk for thyroid cancer?
Women, individuals with a family history of thyroid cancer, and those exposed to radiation have a higher risk.
5. Does surgery always involve removing the entire thyroid gland?
Not necessarily. In some cases, only part of the thyroid (lobectomy) may be removed.