Overview
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease and a leading cause of death worldwide.
It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (a combination of cholesterol, fat, and other substances).
This condition can lead to reduced blood flow to the heart, causing chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms. If left untreated, CAD can result in serious complications, including heart attacks and heart failure.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for CAD is crucial for maintaining heart health and preventing life-threatening outcomes.
Table of Contents
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
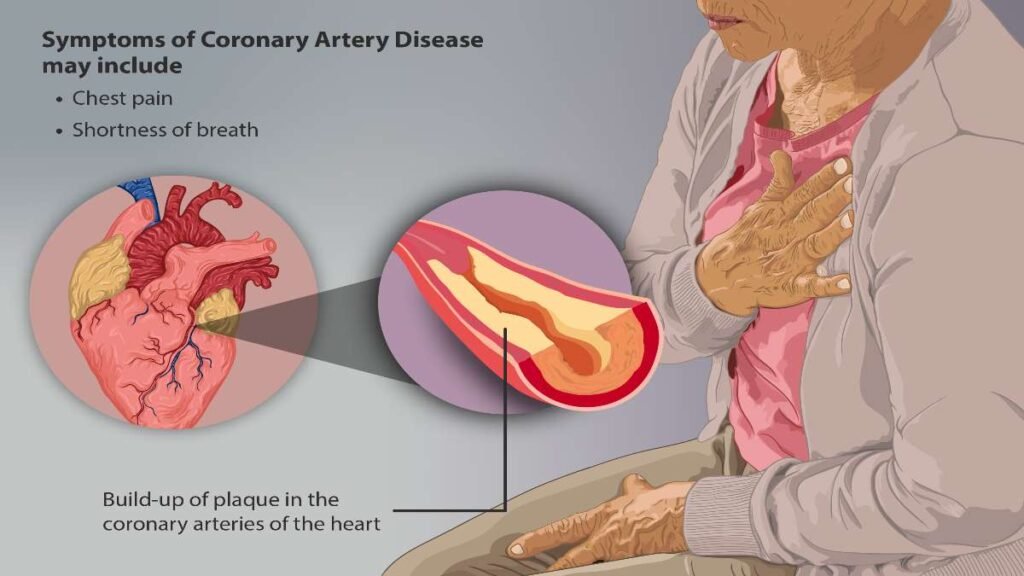
Coronary Artery Disease, also known as coronary heart disease (CHD), develops when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis.
This buildup narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart. Over time, the plaque can harden or rupture, potentially leading to a heart attack.
CAD typically develops over many years and may go unnoticed until significant artery blockage occurs.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
The symptoms of CAD can vary from mild to severe and may differ between individuals. Common symptoms include:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort (Angina): A common symptom of CAD, characterized by a feeling of pressure, tightness, or pain in the chest, especially during physical activity or stress. Angina may radiate to the shoulders, arms, neck, or jaw.
- Shortness of Breath: Reduced blood flow to the heart can lead to breathlessness, especially during exertion or physical activity.
- Fatigue: Decreased oxygen supply to the heart can cause unexplained fatigue, even during routine activities.
- Heart Palpitations: Irregular or rapid heartbeats may occur due to insufficient blood flow.
- Nausea or Lightheadedness: In some cases, individuals may experience dizziness, nausea, or cold sweats.
- Silent Ischemia: Some individuals may have no noticeable symptoms, a condition known as silent ischemia, which can increase the risk of a heart attack.
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
Several factors contribute to the development of CAD, including:
- Atherosclerosis: The primary cause of CAD, atherosclerosis involves the buildup of plaque in the arterial walls, leading to narrowed or blocked arteries.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Chronic high blood pressure can damage arterial walls, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
- High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol, contribute to plaque formation.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke damages blood vessels and accelerates the buildup of plaque, increasing the risk of CAD.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage arteries and promote atherosclerosis.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases the risk of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and diabetes, all of which contribute to CAD.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is a significant risk factor for CAD, as it contributes to obesity and poor cardiovascular health.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease increases the likelihood of developing CAD.
- Stress: Chronic stress can elevate blood pressure and contribute to unhealthy lifestyle habits, such as smoking or overeating.
Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease
Certain risk factors increase the likelihood of developing CAD, including:
- Age: The risk of CAD increases with age, particularly after 45 in men and after 55 in women.
- Gender: Men are generally at a higher risk of CAD, though the risk increases for women after menopause.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, salt, and sugar contribute to the development of CAD.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy drinking can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart disease.
Complications of Coronary Artery Disease
If left untreated, CAD can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A complete blockage of a coronary artery can lead to a heart attack, causing permanent heart damage.
- Heart Failure: Reduced blood flow weakens the heart, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats can develop due to insufficient blood flow.
- Stroke: Plaque buildup can lead to blood clots, increasing the risk of stroke.
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease
To diagnose CAD, healthcare providers use a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical activity of the heart and detects abnormalities in heart rhythm.
- Stress Test: Monitors the heart’s performance during physical exertion to identify reduced blood flow.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to create images of the heart and assess its function.
- Coronary Angiography: An imaging test that uses contrast dye and X-rays to visualize blockages in the coronary arteries.
- Blood Tests: Measures cholesterol, blood sugar, and other markers associated with heart disease.
- CT Coronary Angiogram: A non-invasive imaging test that provides detailed images of the coronary arteries.
Treatment for Coronary Artery Disease
The treatment of CAD aims to manage symptoms, reduce risk factors, and prevent complications. Common treatment options include:
1. Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet: A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can reduce cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in moderate physical activity for at least 30 minutes most days of the week improves cardiovascular health.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking reduces the risk of further artery damage and improves heart function.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and counseling can help manage stress and reduce heart disease risk.
2. Medications:
- Antiplatelet Drugs (e.g., Aspirin): Prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of heart attack.
- Cholesterol-Lowering Medications (e.g., Statins): Lower LDL cholesterol and reduce plaque buildup.
- Beta-Blockers: Reduce heart rate and blood pressure, decreasing the heart’s workload.
- ACE Inhibitors: Lower blood pressure and protect blood vessels.
- Nitrates: Relieve chest pain by dilating blood vessels and improving blood flow.
3. Surgical Procedures:
- Coronary Angioplasty and Stent Placement: A minimally invasive procedure to open blocked arteries and insert a stent to keep them open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical procedure that creates a new pathway for blood to flow around blocked arteries.
Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease
Preventing CAD involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors:
- Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and added sugars.
- Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight through diet and exercise.
- Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco products and seek support if needed to quit.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine.
- Monitor and Control Medical Conditions: Regularly check and manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Coronary Artery Disease is a significant health concern that requires early diagnosis and effective management to prevent life-threatening complications.
By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can reduce their risk of CAD and maintain optimal heart health.
FAQs
1. How to reduce coronary artery blockage?
Reducing coronary artery blockage involves lifestyle changes, dietary improvements, and medical management.
Start by following a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, while avoiding saturated fats, trans fats, and excessive salt.
Regular physical activity, such as 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days, is essential. Quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and managing stress through relaxation techniques further improve heart health.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, controlling blood pressure, and managing diabetes are crucial. In some cases, medications like statins or medical procedures like angioplasty may be necessary, depending on the severity of the blockage.
2. Can you stop CAD from getting worse?
Yes, coronary artery disease (CAD) can be managed to prevent it from worsening. Key strategies include:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Managing risk factors: Controlling blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Medications: Statins, blood thinners, and antihypertensive drugs may help manage CAD progression.
- Stress reduction: Engaging in stress-relief practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- Regular check-ups: Monitoring heart health with medical guidance can catch issues early and prevent further damage.
3. What are 5 symptoms of coronary heart disease?
Early signs include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, heart palpitations, and nausea or lightheadedness
4. Can CAD be reversed?
Coronary artery disease (CAD) cannot be fully reversed, but its progression can be slowed or stabilized. Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, managing risk factors, and taking prescribed medications can reduce plaque buildup and improve heart function. In some cases, interventions like angioplasty can help restore blood flow.
5. Is CAD hereditary?
Yes, coronary artery disease (CAD) can be hereditary. A family history of heart disease increases the risk of developing CAD, as genetic factors may contribute to conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. However, lifestyle changes can help manage and reduce the risk of CAD.
6. Can diet alone manage CAD?
A heart-healthy diet is essential but often needs to be combined with exercise, medications, and other interventions.