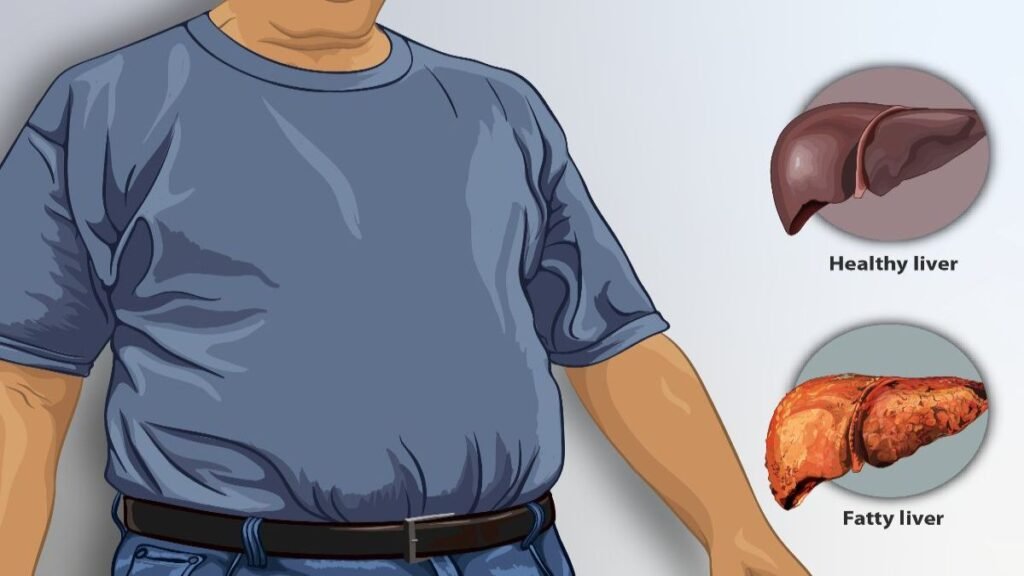
What is fatty liver disease (FLD)?
Fatty liver disease (FLD) is a condition that occurs when fats build up in your liver. It is one of the most common chronic liver diseases. It is also known as hepatic steatosis.
The liver is the second largest organ in your body that helps you digest nutrients from food and drinks, store energy, and filter toxic substances from your blood.
Extra build-up of fats makes it harder for your liver to work. It can cause inflammation, and cell damage in your liver and create liver scarring, also known as fibrosis.
Severe liver scarring can lead to liver failure, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate liver transplant.
Table of Contents
Types of fatty liver disease:
Depending on the causes of fatty liver, there are two main types of fatty liver disease:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD)
1. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD):
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition that is not caused by heavy drinking of alcohol.NAFLD is very common in the U.S., which affects every 1 out of 3 people.
There are two main kinds of Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
- Simple fatty liver: In simple fatty liver, you have fats in your liver but with little or no inflammation or cell damage in your liver. It does not get worse to cause liver complications. Most people with NAFLD have simple fatty liver.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): In nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, you have inflammation and cell damage in your liver along with fats. It is the advanced stage of fatty liver disease that can cause fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver.
Fibrosis or scarring can lead to cirrhosis and can cause liver failure. About 20% of people with NAFLD suffer from NASH.
2. Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD):
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by the heavy consumption of alcohol. This type is less common and affects 5% of people living in the U.S.
Your liver breaks down the alcohol you drink to remove it from your body. However, the process of breaking it down can generate harmful substances that can damage liver cells, promote inflammation, and weaken your body’s natural defenses.
It usually gets better if you stop drinking alcohol soon enough. If you keep drinking, ALD can cause more serious problems in the next stages.
The next stages are alcoholic hepatitis (also known as Alcoholic steatohepatitis) and cirrhosis.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: In alcoholic hepatitis, you have inflammation or swelling in your liver that can cause fever, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice. And if it’s not treated properly, it can cause liver fibrosis.
- Alcoholic Cirrhosis: In alcoholic cirrhosis, there is a buildup of scar tissue in your liver. It can lead to liver failure.
Symptoms of alcoholic cirrhosis include:
- High blood pressure in the liver
- Large amounts of fluid buildup in your belly
- Bleeding in your body
- Confusion and changes in behavior
Symptoms:
Both nonalcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver diseases are generally silent diseases with few or no symptoms. However, some people may have signs such as tiredness or pain in the upper side of the belly.
If you are suffering from NASH or cirrhosis, you may experience some symptoms including:
- Inflammation in the belly
- Nausea, loss of weight and appetite
- Tiredness or confused behavior
- Yellowish skin and eyes due to jaundice
Causes:
In alcoholic fatty liver disease, the cause is heavy consumption of alcohol.
Heavy consumption of alcohol can alter certain metabolic processes in the liver and some of these metabolic products can combine with fatty acids, leading to the formation of fats in the liver.
But in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the cause is less clear or unknown.
However, this disease is more common in people who have obesity, type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, high levels of bad cholesterol, certain infections, and a family history of liver disease.
Risk factors for fatty liver disease:
In the case of AFLD, the most common cause of it is heavy use of alcohol. Apart from heavy consumption of alcohol, other risk factors include:
- Obesity
- Old age
- Genetics
- Lack of nutrition
- Certain infections like chronic viral hepatitis, especially hepatitis C
The cause of NAFLD is unknown but researchers have found it is more common in people if they:
- Have obesity or overweight
- Have type 2 diabetes and prediabetes
- Have high levels of triglycerides or bad cholesterol (LDL)
- Have high blood pressure
- Have certain infections, such as hepatitis C
- Have lost weight rapidly
- Are older
- Are suffering from certain metabolic syndrome including metabolic syndrome
- Have been exposed to some toxins
- Have polycystic ovary syndrome
- Have a family history of liver disease
How is fatty liver disease diagnosed?
Often most people don’t get symptoms, it is not easy to find fatty liver disease. Your doctor may use different methods to find out you have fatty liver disease.
For diagnosing your fatty liver, your doctor may use the following methods:
1. Medical History
As a part of the medical history, your doctor will ask about your alcohol consumption which will help the doctor to find out whether the fats in your liver are a sign of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
The doctor will ask about the medications you take, your medical conditions, and even your family medical history, including any history of liver disease.
2. Physical Exam:
In the physical exam, your doctor will check your weight and height to calculate your body mass index (BMI). Your BMI determines your weight based on your height.
The doctor will examine your body for signs of fatty liver disease such as an enlarged liver or jaundice.
3. Blood Tests:
In many cases, fatty liver disease is diagnosed after taking your blood tests.
Your doctor might recommend following blood tests to determine the fatty liver disease.
- Liver function tests- to determine the damage to your liver.
- Fibrosis assessment tests- to determine the level of liver scarring (fibrosis).
- Lipid profile tests- to determine the fats such as cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood.
- Alanine aminotransferase test (ALT)- to determine the level of liver enzymes in your blood. Your liver cells contain proteins which are called enzymes. When your liver cells are damaged, the enzymes are released into your bloodstream. If your liver is damaged, the level of these enzymes will be higher than normal.
4. Imaging Tests:
You may go for imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI to determine the fats and stiffness in your liver. Liver stiffness can mean fibrosis, which is scarring of the liver.
5. Liver Biopsy:
In a liver biopsy, a doctor will insert a needle into your liver and remove a piece of tissue for examination of the liver inflammation or liver damage.
Your doctor will give you a local anesthetic to help you relax or control the pain. A liver biopsy is the only way for doctors to diagnose NASH.
How is the fatty liver treated?
In the case of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the first line of treatment is weight loss. Weight loss helps reduce fats, inflammation, and scarring in your liver.
If your doctor thinks that a certain medicine is the cause of your NAFLD, you should stop taking that medicine after getting permission from your doctor.
One drug, remetirom (Rezdiffra), has been approved to treat NASH in addition to diet and exercise.
In the case of alcoholic fatty liver disease, the most important part of treatment is to stop drinking alcohol.
If you need help in quitting alcohol, you must see a therapist or participate in a detoxification program. Some medications can reduce your craving or make you feel sick if you drink alcohol.
AFLD and NASH can lead to cirrhosis and several health complications that can be treated by medicines, surgery, and medical procedures.
If cirrhosis leads to liver failure, you need to have a liver transplant.
Role of lifestyle changes in FLD:
Lifestyle changes are the first-line treatment if you have any of the types of fatty liver disease. Here are some lifestyle changes that can help:
- Incorporate exercises into your routine that can help you to lose weight and maintain overall health.
- Get a healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains and limits salt and sugar.
- Get vaccinations for hepatitis A and B, and the flu. The risk of liver failure increases if you have hepatitis A or B along with FLD.
- Avoid alcohol consumption whether you have NAFLD OR AFLD as it can make the complications worse.
- Consult your doctor before taking any medical drugs or supplements.
Prevention:
To prevent fatty liver disease and its potential complications, it’s crucial to follow a healthy lifestyle. Some general prevention tips include:
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Keep your weight in control
- Include exercises for at least 30 minutes in your routine
- Incorporate a healthy diet that is high in fiber, healthy fats, and other essential nutrients.
- Avoid or limit the foods that are high in salt, sugar, saturated fat, trans fat, and refined carbohydrates
- Manage your blood sugar, cholesterol levels, and triglyceride levels
- Protect yourself from viral infections such as hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C
Conclusion:
Fatty liver disease is the buildup of fats in your liver. One type of FLD is caused due to heavy alcohol drinking.
However, the causes of NAFLD are unknown, but it is more common in people who have obesity, type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, high levels of triglycerides, and bad cholesterol.
Certain lifestyle changes including a healthy diet, and exercise can promote liver health and even reverse liver damage if treated in its early stages.