Overview
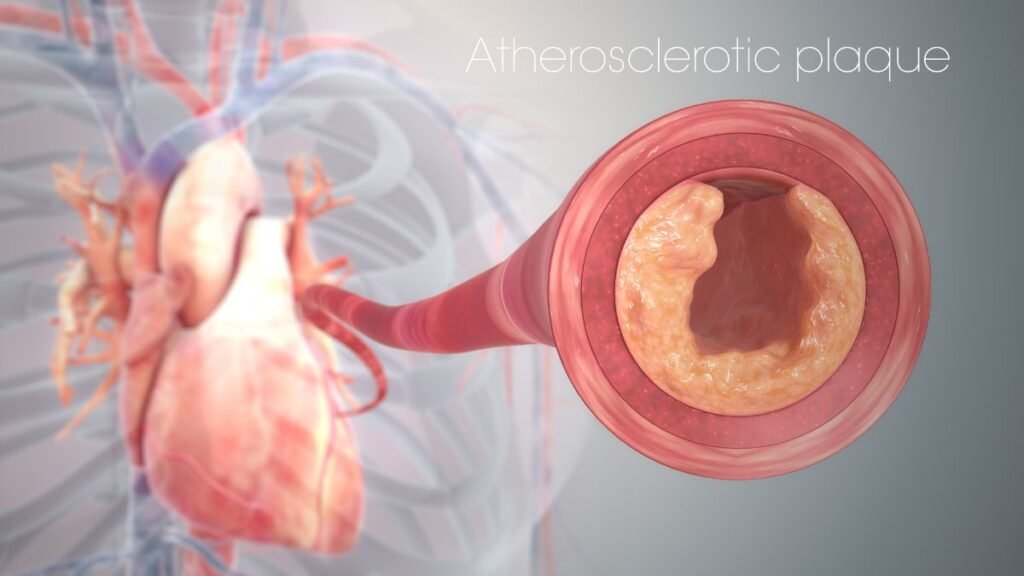
Atherosclerosis is a chronic cardiovascular condition characterized by the buildup of plaque within the arterial walls, leading to the narrowing and hardening of the arteries.
This plaque consists of cholesterol, fatty substances, calcium, and cellular waste, which can obstruct blood flow and trigger serious health complications like heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Often called the “silent killer,” atherosclerosis develops gradually and may remain undetected until a significant cardiovascular event occurs.
Early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications can help manage and prevent its progression.
Table of Contents
What is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis, a general term for the thickening and hardening of arteries.
In atherosclerosis, plaque builds up inside the arteries, causing them to narrow and restrict blood flow to various organs and tissues. This condition can affect any artery in the body but commonly impacts:
- Coronary arteries (leading to coronary artery disease)
- Carotid arteries (leading to stroke)
- Peripheral arteries (leading to peripheral artery disease)
- Renal arteries (leading to kidney dysfunction)
Symptoms of Atherosclerosis
In its early stages, atherosclerosis may not present any noticeable symptoms. However, as the disease progresses and blood flow becomes increasingly restricted, symptoms may appear depending on the affected arteries:
Coronary Arteries (Coronary Artery Disease):
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue during physical activity
Carotid Arteries (Carotid Artery Disease):
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Vision problems in one or both eyes
Peripheral Arteries (Peripheral Artery Disease):
- Leg pain or cramping during walking (claudication)
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Non-healing wounds on the feet or legs
Renal Arteries (Renal Artery Disease):
- High blood pressure that is difficult to control
- Reduced kidney function
Abdominal Aorta (Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm):
- Abdominal or back pain
- A pulsating sensation near the navel
Causes of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a multifactorial disease influenced by various genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. The primary causes include:
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol contribute to plaque formation.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Increased pressure on arterial walls damages the endothelium, promoting plaque buildup.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke damages blood vessels and accelerates atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels contribute to endothelial damage and plaque formation.
- Obesity: Excess body fat increases the risk of high cholesterol, hypertension, and diabetes, all of which contribute to atherosclerosis.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to poor cardiovascular health and plaque buildup.
- Genetics: A family history of atherosclerosis or cardiovascular disease increases the risk.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and refined sugars contribute to high cholesterol and plaque buildup.
Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis
Certain factors increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis, including:
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after 45 for men and 55 for women.
- Gender: Men are generally at a higher risk, although postmenopausal women also face increased risk.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease, stroke, or atherosclerosis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Chronic Inflammation: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and chronic infections can contribute to arterial damage.
Complications of Atherosclerosis
If left untreated, atherosclerosis can lead to severe complications, including:
- Heart Attack: Blockage of coronary arteries can lead to myocardial infarction.
- Stroke: Blockage of carotid arteries can result in ischemic stroke.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Reduced blood flow to the limbs can lead to pain, ulcers, and amputation.
- Aneurysm: Weakened arterial walls may lead to aneurysm formation and rupture.
Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis
Diagnosing atherosclerosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
- Blood Tests: Measure cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, and markers of inflammation like C-reactive protein (CRP).
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detects abnormal heart rhythms and signs of heart disease.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart and assess its function.
- Stress Test: Monitors heart function during physical activity to detect coronary artery disease.
- Doppler Ultrasound: Evaluates blood flow in the peripheral arteries.
- Angiography: Involves injecting contrast dye into the arteries to visualize blockages using X-rays.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): Provides detailed images of the arteries to detect plaque buildup.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to visualize the arteries.
Treatment for Atherosclerosis
The treatment of atherosclerosis focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and slowing disease progression. Treatment options include:
Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet: Adopt a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to improve cardiovascular health.
- Smoking Cessation: Quit smoking to reduce arterial damage and slow disease progression.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of complications.
Medications:
- Statins: Lower LDL cholesterol and stabilize plaque.
- Antihypertensive Drugs: Control high blood pressure to prevent further arterial damage.
- Antiplatelet Agents (e.g., Aspirin): Reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Blood Sugar Control Medications: Manage diabetes to prevent complications.
- Beta-Blockers and ACE Inhibitors: Improve heart function and reduce the risk of heart attack.
Surgical Procedures:
- Angioplasty and Stent Placement: Opens blocked arteries and inserts a stent to keep them open.
- Bypass Surgery: Creates a new pathway for blood flow around a blocked artery.
- Carotid Endarterectomy: Removes plaque from the carotid arteries to prevent stroke.
Prevention of Atherosclerosis
Preventing atherosclerosis involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors:
- Quit Smoking: Avoid tobacco products to protect arterial health.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on heart-healthy foods that lower cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in physical activity to improve circulation and cardiovascular health.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Control diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Aim for a BMI (Body Mass Index) within the healthy range.
- Regular Health Checkups: Monitor cardiovascular health and address risk factors early.
Conclusion
Atherosclerosis is a serious but preventable condition.
By making lifestyle changes, managing chronic conditions, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can reduce their risk of developing atherosclerosis and its complications.
Early detection and proactive management are key to maintaining cardiovascular health and improving quality of life.
FAQs on Atherosclerosis
1. What causes atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is primarily caused by high cholesterol, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes.
2. Can atherosclerosis be reversed?
While it cannot be fully reversed, lifestyle changes and medication can slow its progression and stabilize plaque.
3. What are the symptoms of atherosclerosis?
Symptoms depend on the affected arteries and may include chest pain, leg pain, and shortness of breath.
4. How is atherosclerosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging studies, and physical exams.
5. Is atherosclerosis life-threatening?
Yes, if left untreated, it can lead to heart attack, stroke, and other life-threatening complications.